

At 2 ATA (10m/33ft) a given gas would be 1/2 it's volume, at 3 ATA (20m/66ft) it would be 1/3 it's volume and so on.Boyles Law applies to the diving body's air filled areas such as lungs, sinuses, middle ear, and states that the volume and pressure of a gas at a given temperature are inversely related. Pulmonary barotrauma is precipitated by positive-pressure mechanical ventilation in the setting of underlying lung disease.Pascals Law applies to the diving body (without air filled areas such as lungs) states that the pressure applied to any part of the enclosed liquid will be transmitted equally in all directions through the liquid.It is often associated with haemoptysis, or the spitting of blood in the respiratory tract. pulmonary barotrauma is synonomous with burst lung and pulmonary.
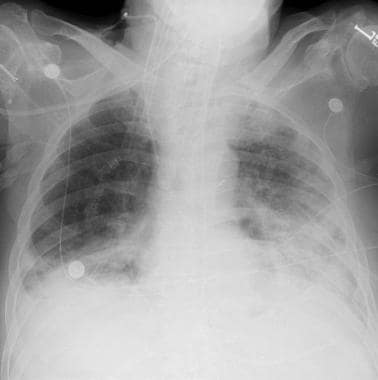
When this occurs, the lungs can fill with fluid and the gas exchange in the alveoli is compromised. V Diagnosis and Treatment of Gas Embolism A. When does barotrauma of the lung occur 1 Pulmonary barotrauma most often occurs during ascent and is due to lung overexpansion when a SCUBA diver returns to the. VILI is a common complication of mechanical ventilation and results in pneumothorax, pneumomediastinum. Factors increasing risk of pulmonary barotrauma include certain. Ventilator-induced lung injury (VILI) is the result of injurious ventilator settings that lead to a combination of barotrauma, volutrauma, atelectrauma (repeated opening and closing of alveoli), or chemotrauma (paracrine inflammatory effects). Barodentalgia (trapped dental air causing squeeze) A lung barotrauma, known as a lung squeeze, is a pressure-related pulmonary oedema. Expert Answers: Barotrauma is tissue injury caused by a pressure-related change in body compartment gas volume.Occurs when diver breathing compressed air ascends too rapidly.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
